Symptoms, remedies, and preventive measures for Polio, a renowned infectious disease, and its related vaccines.
## Title: Global Efforts to Eradicate Polio: Focus on Nigeria, Pakistan, and Afghanistan
Polio, a viral infection that can lead to paralysis and even death, continues to pose a threat in three countries: Nigeria, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. Despite the eradication of polio in almost every other nation, these countries remain the last strongholds of the disease.
### Vaccination Campaigns and Community Engagement
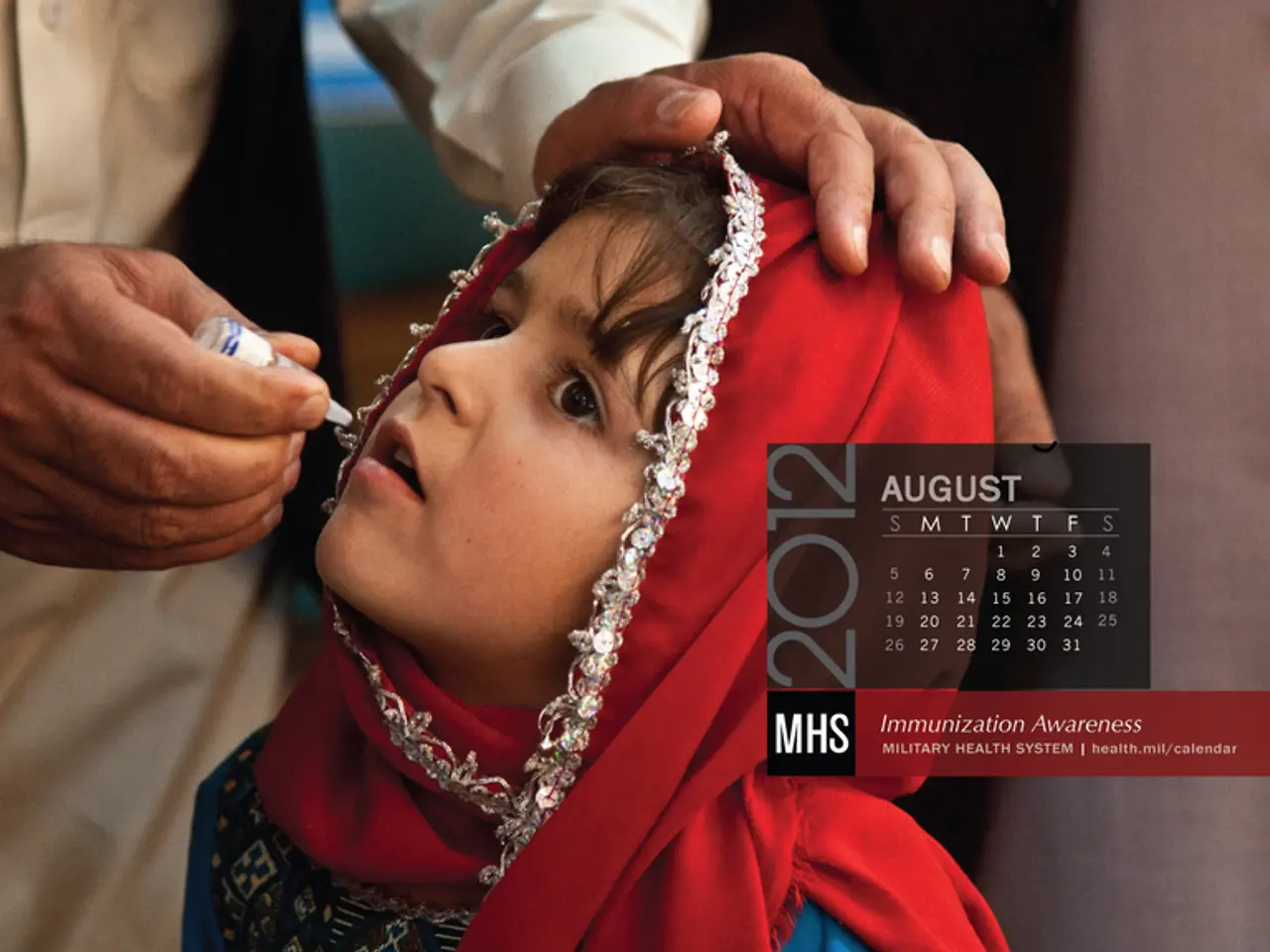
To combat polio, various measures and strategies are being implemented. In Nigeria, the Kano State Government, in collaboration with UNICEF, has planned intensive vaccination campaigns. The goal is to vaccinate 3.9 million children under the age of five during the June 2025 Outbreak Response (OBR) campaign. Frontline workers are engaging with communities to build trust in vaccination initiatives and motivate caregivers to vaccinate their children.
Similar efforts are being made in Pakistan and Afghanistan, with a focus on targeted vaccination efforts, community-based initiatives, and addressing access challenges. In all three countries, the focus is on overcoming challenges such as vaccine hesitancy, security issues, and geographical barriers to ensure successful polio eradication efforts.
### Understanding Polio and Its Risks
Polio is usually contracted through the fecal-oral route, either from contaminated water or food. The polio virus can remain in an infected person's feces for weeks, even if they show no symptoms. The disease can lead to a range of symptoms, from flu-like symptoms that last for a few days or weeks, to paralytic polio, which affects a small percentage of those invaded by the virus and leads to a loss of muscle reflexes, severe muscle pain and spasms, and breathing problems.
It's important to note that there is no cure for polio once a person develops the virus. Treatments are focused on increasing comfort, managing symptoms, and preventing complications. Additionally, around half of the people who have had polio go on to develop post-polio syndrome, a condition that affects up to 64 percent of all polio patients and includes muscle and joint pain and weakness, muscle atrophy or shrinkage, exhaustion, swallowing and breathing difficulties, and no cure.
### Vaccines and Risk Factors
There are two vaccines available to fight polio: the inactivated poliovirus (IPV) vaccine and the oral polio vaccine (OPV). The OPV, which is low cost, easy to administer, and gives an excellent level of immunity, is created from a weakened form of poliovirus. However, OPV has been known to revert to a dangerous form of poliovirus in very rare cases, which is able to cause paralysis.
Additional risk factors for polio include traveling to places where polio is endemic or widespread, especially Pakistan and Afghanistan, living with someone infected with polio, having a weak immune system, being pregnant (although polio does not appear to affect the unborn child), and working in a laboratory where live poliovirus is kept.
In conclusion, global efforts to eradicate polio continue in Nigeria, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. Through vaccination campaigns, community engagement, and addressing access challenges, the World Health Organization (WHO) aims to eliminate polio completely. It's crucial for individuals to be vaccinated against polio and to be aware of the risks and symptoms associated with the disease.
- The oral polio vaccine (OPV), despite being affordable and easy to administer, can revert to a dangerous form in extremely rare cases, potentially causing paralysis.
- In addition to vaccines, factors such as traveling to polio-endemic regions, living with an infected person, having a weak immune system, and being pregnant can increase the risk of contracting polio.
- Despite eradicating polio in almost every nation, the disease continues to pose a threat in neurological-disorders like paralysis in Nigeria, Pakistan, and Afghanistan due to factors like vaccine hesitancy, security issues, and geographical barriers.